Title: The Intricacies of Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts in Law
Introduction: In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital technology, blockchain-based smart contracts are emerging as a transformative force in legal practice. This innovative fusion of code and contract law promises to revolutionize how agreements are executed and enforced. As we delve into this cutting-edge topic, we'll explore the legal implications, challenges, and potential benefits of smart contracts in various sectors.
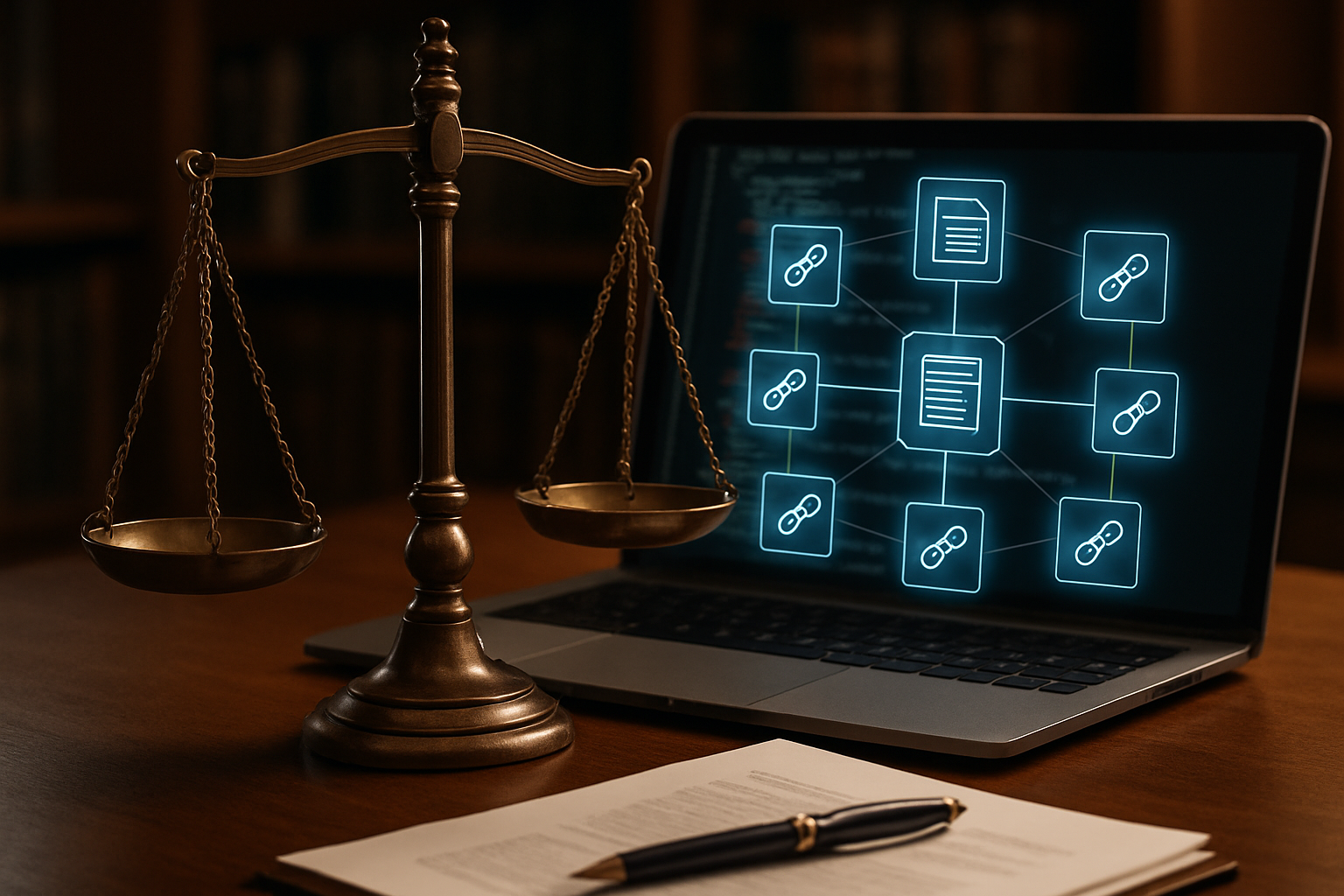

Legal Status and Recognition
The legal status of smart contracts varies across jurisdictions, presenting a complex landscape for lawmakers and legal practitioners. Some states, like Arizona and Tennessee, have passed legislation recognizing smart contracts as legally binding. However, many jurisdictions are still grappling with how to integrate these digital agreements into existing legal frameworks. The challenge lies in reconciling the immutable nature of blockchain with the need for legal flexibility and interpretation.
Enforceability and Dispute Resolution
One of the most pressing issues surrounding smart contracts is their enforceability. While the code itself executes automatically, questions arise when disputes occur or when external factors affect the contract’s performance. Traditional contract law principles such as mistake, duress, and unconscionability may be challenging to apply to smart contracts. Courts and arbitrators are now faced with the task of developing new approaches to resolve disputes arising from these digital agreements.
Smart Contracts in Specific Legal Domains
The potential applications of smart contracts span various legal domains. In intellectual property law, smart contracts could automate royalty payments and licensing agreements, ensuring more transparent and efficient distribution of rights and revenues. In real estate, they could streamline property transfers and automate rental agreements. Corporate law could see the implementation of smart contracts in shareholder voting and dividend distribution, potentially increasing transparency and reducing administrative burdens.
Regulatory Challenges and Compliance
As smart contracts gain prominence, regulators face the challenge of ensuring these digital agreements comply with existing laws and regulations. Anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements present particular challenges in the context of decentralized, autonomous contracts. Regulators must strike a balance between fostering innovation and protecting consumers and market integrity. The development of regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions may play a crucial role in addressing these compliance challenges.
The Role of Legal Professionals in the Smart Contract Era
The advent of smart contracts is reshaping the role of legal professionals. Lawyers must now develop a new skill set that combines legal expertise with an understanding of blockchain technology and coding principles. This shift is giving rise to a new breed of legal professionals often referred to as legal engineers or legal technologists. Law schools and continuing legal education programs are increasingly incorporating blockchain and smart contract courses to prepare the next generation of lawyers for this digital transformation.
Ethical Considerations and Professional Responsibility
Smart contracts raise novel ethical considerations for legal practitioners. The immutability of blockchain transactions and the potential for automated execution of legal agreements challenge traditional notions of attorney-client relationships and professional responsibility. Lawyers must navigate issues such as client confidentiality in a transparent blockchain environment and their duty to advise clients on the risks and benefits of smart contracts. The legal profession’s ethical guidelines may need to evolve to address these new technological realities.
The Future of Smart Contracts in Law
As blockchain technology continues to mature, the integration of smart contracts into legal practice is likely to accelerate. We may see the development of hybrid systems that combine the automation of smart contracts with traditional legal safeguards. The potential for smart contracts to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance transparency in legal transactions is significant. However, their widespread adoption will depend on overcoming technical, legal, and regulatory hurdles.
In conclusion, blockchain-based smart contracts represent a frontier in legal innovation, offering both exciting possibilities and complex challenges. As the legal community grapples with this emerging technology, it is clear that smart contracts will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of law and legal practice. The coming years will be crucial in determining how these digital agreements are integrated into our legal systems and what new legal paradigms may emerge as a result.