The role of judiciary in a democratic society
The judiciary serves as a cornerstone of any democratic society, playing a vital role in upholding the rule of law and ensuring justice for all citizens. Its independence and impartiality are essential for maintaining public trust and safeguarding the fundamental rights and freedoms that define a democracy. This branch of government acts as a crucial check on the powers of the executive and legislative branches, creating a balanced system of governance.
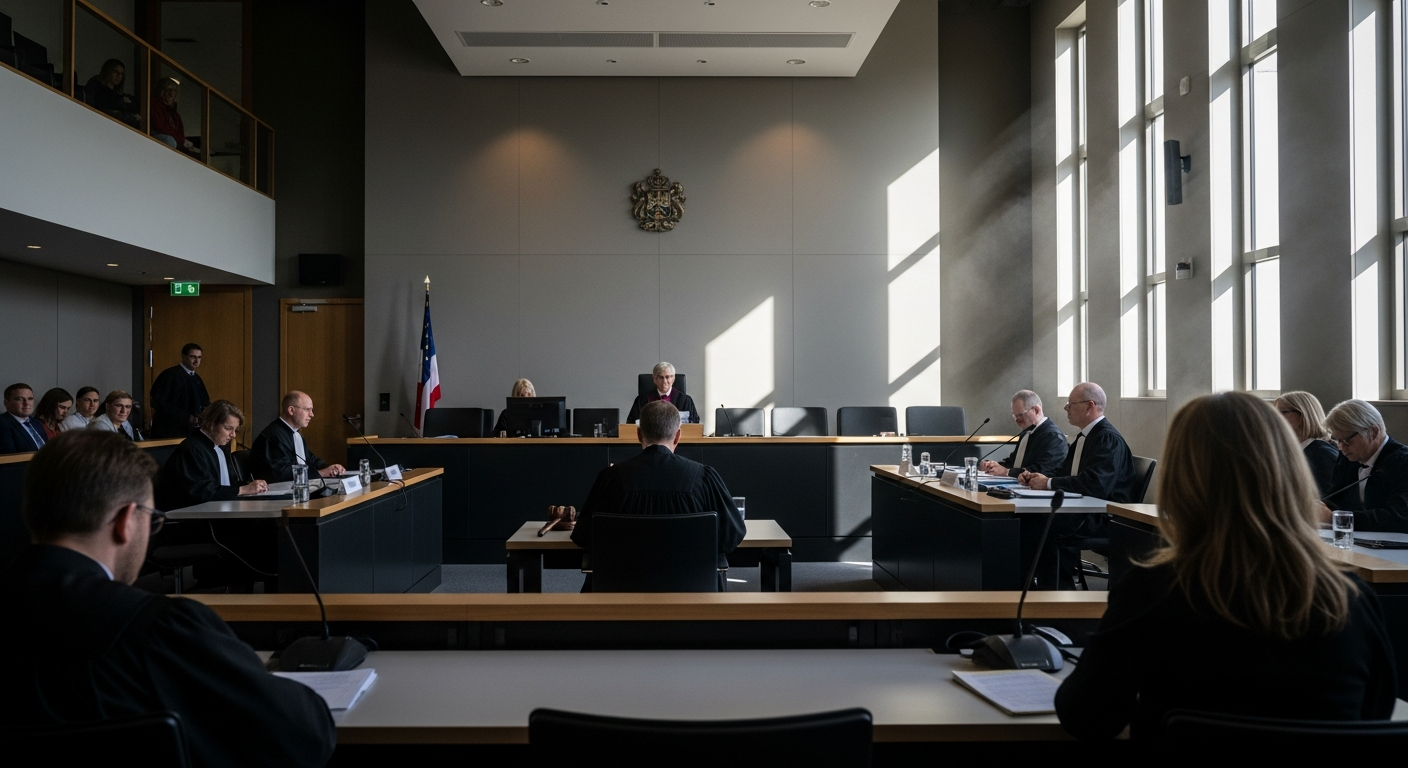

The judiciary’s function extends far beyond simply resolving disputes; it is integral to the very fabric of a democratic nation. By interpreting laws and applying them fairly, the judicial system ensures that the principles enshrined in a country’s constitution are respected and upheld. This foundational role helps to maintain order, protect individual liberties, and foster a society where justice is accessible to everyone.
Ensuring Justice and Protecting Citizen Rights
At its core, the judiciary is responsible for dispensing justice. This involves interpreting legislation and applying it to specific cases, ensuring that every citizen receives fair treatment under the law. It acts as the ultimate guarantor of individual rights, safeguarding freedoms such as speech, assembly, and due process. Through its rulings, the judiciary ensures that public authority adheres to established legal frameworks, preventing arbitrary actions and protecting citizens from potential overreach by the state or other powerful entities. This commitment to justice is fundamental to maintaining citizen confidence in the legal system.
Interpreting Regulation and Legislation
One of the most critical tasks of the judiciary is the interpretation of regulation and legislation. Laws, whether they are statutes passed by the legislature or policies enacted by the executive, often require careful interpretation to be applied correctly in diverse situations. Judges analyze the text, intent, and context of these laws to make informed decisions. This process ensures that laws are applied consistently and fairly, providing clarity and predictability within the legal system. The judiciary’s ability to interpret law also allows it to adapt existing legislation to new circumstances, ensuring the legal framework remains relevant.
Upholding the Constitutional Framework and Governance
In a democratic society, the constitution forms the supreme law of the land, outlining the structure of governance and the rights of its people. The judiciary plays a pivotal role in upholding this constitutional framework. Through judicial review, courts can examine whether legislative acts or executive actions comply with constitutional provisions. This power is crucial for maintaining the balance of power among the different branches of government and for safeguarding democratic principles. By ensuring adherence to the constitution, the judiciary contributes significantly to good governance and the stability of the state.
Judicial Authority and Enforcement of Statutes
The authority of the judiciary is derived from the constitution and the laws it interprets. Its decisions, once final, are binding and must be respected by all parties, including the government. The enforcement of statutes and court orders is a critical aspect of the judiciary’s role. Without effective enforcement, judicial pronouncements would lack impact, undermining the rule of law. While the judiciary typically relies on the executive branch for physical enforcement, its inherent authority ensures that its judgments carry significant weight and are generally complied with, maintaining the integrity of the legal system.
Fostering Public Trust and Accountability
The effectiveness of the judiciary in a democratic society largely depends on the public’s trust in its impartiality and fairness. Judicial independence—the principle that judges should be free from political interference and external pressure—is paramount for maintaining this trust. Furthermore, the judiciary must operate with a degree of accountability, ensuring that its processes are transparent and that judges uphold ethical standards. This balance between independence and accountability helps to legitimize judicial decisions and reinforces the public’s belief in the legal system as a fair and reliable arbiter of disputes.
In conclusion, the judiciary is an indispensable pillar of a democratic society. Its multifaceted role encompasses ensuring justice, protecting fundamental rights, interpreting laws, upholding the constitution, and enforcing legal norms. Through its independent and impartial functions, the judiciary provides a vital check on governmental power, maintains the rule of law, and ultimately contributes to the stability and health of the entire democratic system, fostering a society where law and order prevail and citizens can live with confidence in their legal protections.