Neolocalism: The Rebirth of Community in a Global Age
In an era of unprecedented global connectivity, a surprising trend is taking root across communities worldwide. Neolocalism, a movement championing local identity and community engagement, is reshaping how people interact with their immediate surroundings. This article delves into the rise of neolocalism, its impact on social structures, and its potential to redefine our sense of belonging in an increasingly interconnected world. Read below to explore this fascinating societal shift.
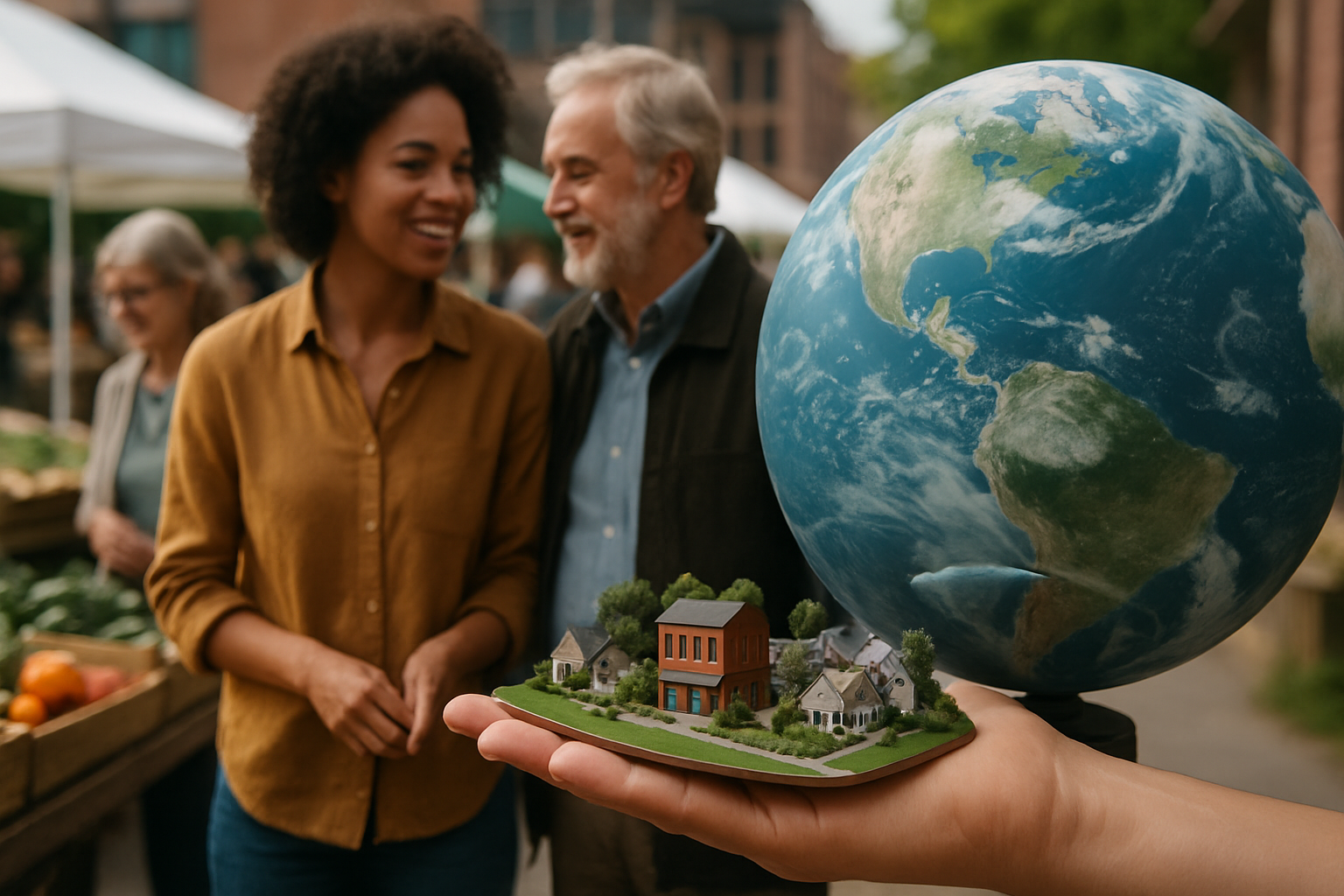

The concept of neolocalism builds upon earlier ideas of localism but adapts them to the modern, globalized context. Unlike traditional localism, which often resisted outside influences, neolocalism embraces a hybrid approach. It seeks to preserve and celebrate local distinctiveness while simultaneously acknowledging the benefits of global interconnectedness.
The Pillars of Neolocalism
Neolocalism is characterized by several key elements that distinguish it from other social movements:
-
Local Economic Support: Emphasis on patronizing local businesses, artisans, and farmers.
-
Cultural Preservation: Efforts to maintain and promote local traditions, languages, and customs.
-
Environmental Stewardship: Focus on sustainable practices and protection of local ecosystems.
-
Community Engagement: Active participation in local governance and community-building initiatives.
-
Place-Based Education: Integration of local history, ecology, and culture into educational curricula.
These pillars work together to create a holistic approach to community development that balances local needs with global realities.
Neolocalism in the Digital Age
Paradoxically, the digital revolution has played a crucial role in the spread of neolocalism. Social media platforms and online communities have enabled like-minded individuals to connect, share ideas, and organize local initiatives on a scale previously unimaginable. This digital infrastructure has allowed neolocal movements to transcend geographical boundaries while still maintaining their focus on local action.
The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated this trend, as lockdowns and travel restrictions forced people to rediscover their immediate surroundings. Many found solace in supporting local businesses, exploring nearby natural areas, and connecting with neighbors through online platforms. This renewed appreciation for the local has had lasting effects on consumer behavior and community engagement.
Economic Implications of Neolocalism
The neolocal movement has significant economic implications, challenging traditional models of globalized commerce. Local currencies, time banks, and community-supported agriculture are just a few examples of alternative economic systems that have gained traction under the neolocal banner.
Research by the New Economics Foundation has shown that money spent at local businesses circulates within the community up to three times longer compared to money spent at chain stores. This multiplier effect can lead to increased local employment, improved public services, and a more resilient local economy.
However, critics argue that an overemphasis on local economies may lead to protectionism and hinder global economic growth. Striking a balance between local support and global trade remains a key challenge for policymakers and community leaders.
Cultural Identity in a Neolocal World
One of the most profound impacts of neolocalism is its influence on cultural identity. As globalization threatened to create a monoculture, neolocalism has emerged as a counterforce, celebrating the unique characteristics of individual places and communities.
This renewed focus on local identity has led to a resurgence of interest in regional dialects, traditional crafts, and local festivals. Sociologists have observed that this trend is particularly strong among younger generations, who are seeking authentic experiences and connections in an increasingly digital world.
However, the neolocal emphasis on cultural distinctiveness also raises questions about inclusivity and the potential for exclusionary practices. Balancing the preservation of local traditions with openness to diversity and change is an ongoing challenge for neolocal movements.
The Future of Neolocalism
As we look to the future, neolocalism is likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping social, economic, and environmental policies. Urban planners are already incorporating neolocal principles into their designs, creating walkable neighborhoods with mixed-use developments that foster community interaction and local economic activity.
The movement also has the potential to address some of the most pressing global challenges, such as climate change and social inequality, by promoting sustainable practices and community-based solutions. However, for neolocalism to truly thrive, it must continue to evolve and adapt to changing technological and social landscapes.
In conclusion, neolocalism represents a fascinating reimagining of community in the 21st century. By blending local action with global awareness, it offers a pathway to more resilient, sustainable, and connected communities. As this movement continues to grow and evolve, it may well shape the future of how we live, work, and interact with the world around us.