Harnessing the Power of Hydrogen: The Future of Fuel Cell Vehicles
In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive technology, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are emerging as a promising alternative to traditional combustion engines. This innovative propulsion system combines the eco-friendly benefits of electric vehicles with the convenience and range of conventional cars. As automakers and governments worldwide invest heavily in hydrogen infrastructure and research, fuel cell vehicles are poised to revolutionize the way we think about clean transportation.

The Science Behind Hydrogen Fuel Cells
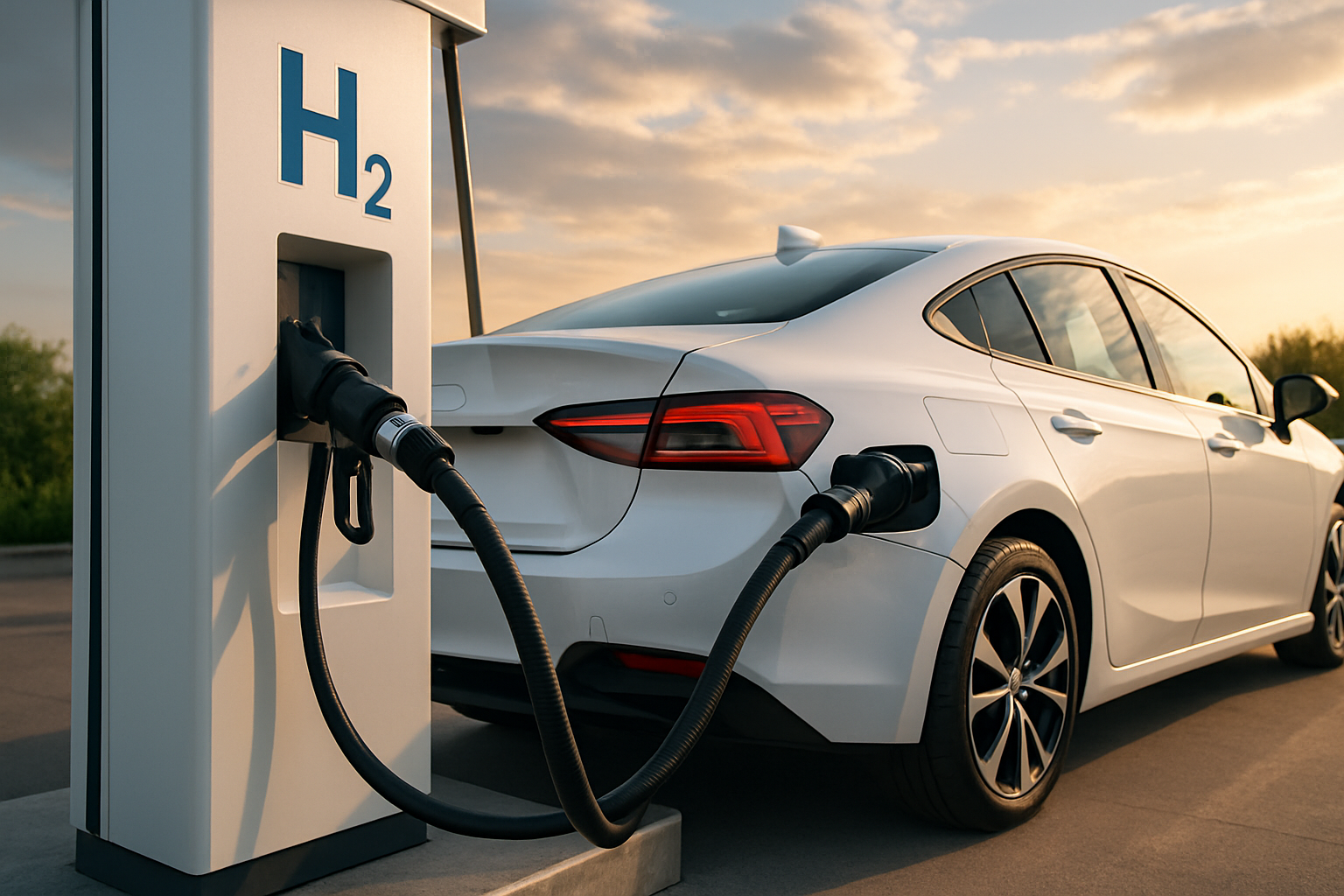
At the heart of every fuel cell vehicle lies a complex yet elegant system that converts chemical energy into electrical power. The process begins with hydrogen stored in high-pressure tanks within the vehicle. This hydrogen is fed into the fuel cell stack, where it undergoes a chemical reaction with oxygen from the air. The result? Electricity to power the vehicle’s motors and water vapor as the only byproduct.
Unlike battery-electric vehicles, fuel cell cars can be refueled in minutes, offering a range comparable to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. This quick refueling time and extended range make hydrogen fuel cell technology particularly attractive for long-distance travel and commercial applications.
The Environmental Impact
One of the most compelling arguments for hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is their potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When powered by hydrogen produced from renewable sources, these vehicles operate with a near-zero carbon footprint. This makes them an essential tool in the fight against climate change and air pollution in urban areas.
However, it’s important to note that the environmental benefits of hydrogen fuel cells depend heavily on how the hydrogen is produced. Currently, most hydrogen is derived from natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming, which does produce some carbon emissions. The challenge lies in scaling up green hydrogen production methods, such as electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources.
Infrastructure and Adoption Challenges
Despite the promising technology, widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles faces several hurdles. The most significant challenge is the lack of refueling infrastructure. Unlike electric charging stations, which can be installed relatively easily, hydrogen fueling stations require substantial investment and specialized equipment.
Another obstacle is the high cost of fuel cell technology. While prices have decreased significantly in recent years, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles remain more expensive than their battery-electric counterparts. However, as production scales up and technology improves, these costs are expected to decline, making fuel cell vehicles more accessible to the average consumer.
Industry Leaders and Innovations
Several major automakers have thrown their weight behind hydrogen fuel cell technology. Toyota, with its Mirai model, has been at the forefront of commercializing fuel cell vehicles. Honda and Hyundai have also entered the market with their own offerings, while other manufacturers are developing fuel cell systems for heavy-duty trucks and buses.
Innovation in this field extends beyond just passenger vehicles. Companies are exploring the use of fuel cells in everything from forklifts to trains and even aircraft. This diversification of applications is driving further research and development, potentially leading to breakthroughs that could accelerate adoption across various sectors.
The Role of Government and Policy
Government support plays a crucial role in the development and adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology. Countries like Japan, South Korea, and Germany have implemented ambitious hydrogen strategies, offering incentives for both consumers and businesses to invest in fuel cell vehicles and infrastructure.
In the United States, California has been leading the charge, with plans to have 200 hydrogen fueling stations operational by 2025. These initiatives are essential for creating the ecosystem necessary for hydrogen fuel cell vehicles to thrive, demonstrating the importance of public-private partnerships in advancing clean energy technologies.
The Future Outlook
As we look to the future, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are poised to play a significant role in the transition to sustainable transportation. While they may not replace battery-electric vehicles entirely, fuel cells offer unique advantages that make them well-suited for certain applications, particularly in the realm of long-distance and heavy-duty transport.
The success of hydrogen fuel cell technology will depend on continued investment in research and development, expansion of refueling infrastructure, and supportive government policies. As these elements come together, we may see a future where hydrogen-powered vehicles are as common on our roads as gasoline cars are today, ushering in a new era of clean, efficient, and sustainable transportation.
In conclusion, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles represent a fascinating convergence of advanced technology and environmental consciousness. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, these innovative vehicles offer a glimpse into a future where clean energy and high performance go hand in hand. While challenges remain, the potential benefits of widespread adoption make hydrogen fuel cells a technology worth watching in the years to come.