Automation's Impact on Production Workflows
Automation is fundamentally reshaping production workflows across various industries, introducing significant changes to how goods are manufactured, processed, and distributed. This transformative shift goes beyond simply replacing manual labor; it involves integrating advanced technologies to enhance precision, speed, and overall operational effectiveness. Understanding the scope of automation's influence is crucial for businesses aiming to maintain competitiveness and adapt to evolving industrial landscapes.
Enhancing Manufacturing and Production through Automation
Automation plays a pivotal role in modern manufacturing and production processes by streamlining repetitive tasks and improving operational consistency. Automated systems, such as robotic arms and CNC machines, can perform complex operations with high accuracy, reducing human error and increasing output quality. This integration allows for continuous operation, often 24/7, which significantly boosts production volumes and accelerates lead times. The ability to execute precise movements repeatedly ensures a uniform product, which is essential for industries requiring strict quality control. Furthermore, automated data collection within these systems provides valuable insights into performance, enabling continuous optimization of manufacturing lines.
Optimizing Operations and Logistics with Advanced Technology
The application of advanced technology in operations and logistics has revolutionized how materials and products move through the supply chain. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are increasingly used in warehouses and factories to transport goods, manage inventory, and sort packages efficiently. These systems minimize manual handling, reduce the risk of workplace injuries, and improve the speed of order fulfillment. Predictive analytics, powered by automation, can forecast demand more accurately, leading to optimized inventory levels and reduced waste. This integration of technology across logistics networks not only enhances responsiveness but also contributes to a more resilient and agile supply chain capable of adapting to market fluctuations.
Driving Efficiency and Sustainability in Production Workflows
Automation is a key driver of efficiency and sustainability within production workflows. By optimizing resource allocation and minimizing waste, automated processes contribute to more environmentally responsible operations. For example, precise robotic applications in painting or welding can reduce material consumption and energy usage compared to manual methods. Furthermore, the data generated by automated systems allows companies to monitor energy consumption patterns and identify areas for improvement, fostering greater sustainability. This focus on efficiency extends to reducing rework and scrap rates, which not only saves resources but also lowers operational costs, promoting long-term growth and environmental stewardship.
Transforming the Workforce and Fostering Digital Growth
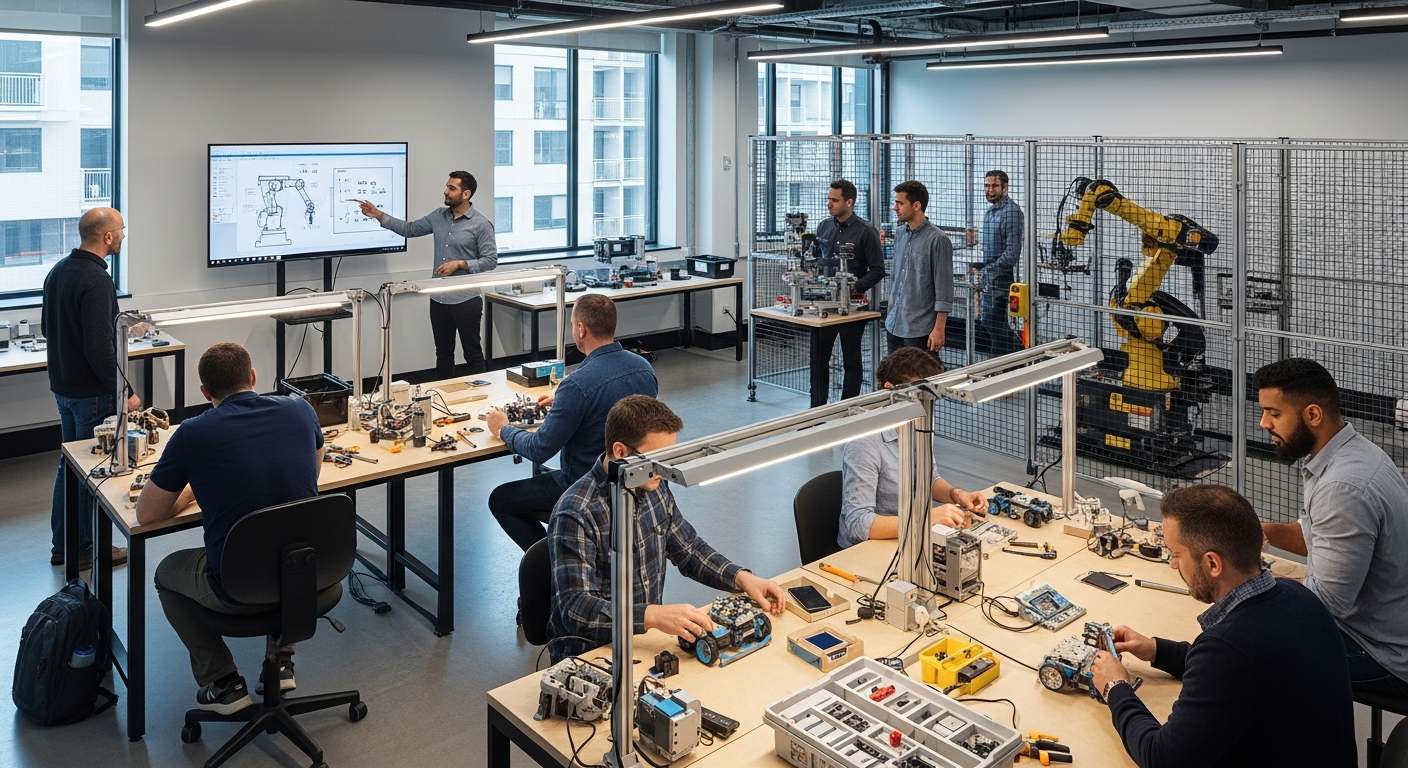
The introduction of automation significantly impacts the workforce, shifting the demand from manual, repetitive tasks to roles requiring oversight, maintenance, and programming of automated systems. This transformation necessitates upskilling and reskilling initiatives to prepare employees for new responsibilities in a digital environment. While some jobs may be automated, new roles often emerge in areas such as robotics engineering, data analytics, and system integration. For an enterprise, embracing automation means fostering a culture of continuous learning and adapting to digital tools, which ultimately drives growth and innovation. Human workers transition to higher-value activities, focusing on problem-solving, creativity, and strategic decision-making, complementing the capabilities of machines.
Building Resilience and Innovation in the Global Industrial Landscape
Automation enhances resilience and fosters innovation within the global industrial landscape by enabling companies to respond quickly to disruptions and market changes. Automated production lines can be reprogrammed and reconfigured more rapidly than traditional setups, allowing businesses to pivot production to meet evolving consumer demands or supply chain challenges. This flexibility is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage in a dynamic market. Furthermore, the data collected by automated systems provides a rich source for analysis, fueling innovation in product design, process improvement, and service delivery. For industry and commerce, automation is not just about current production but also about building future capabilities and ensuring long-term development in an interconnected world.